Today, we will explore the key differences between two essential tools in any handyman’s toolkit: the power screwdriver and the impact driver. While both are designed to make your life easier when it comes to driving screws, they have distinct features and functions that set them apart. By understanding these differences, you can choose the right tool for your specific needs and tackle any project with confidence. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of power screwdrivers and impact drivers, and discover the nuances that make each tool unique.
Power Screwdriver
Definition:
A power screwdriver is a versatile tool that is designed to drive screws into various materials with ease. It is equipped with a motor that provides rotational force, allowing for quick and efficient screwdriving.
Function:
The primary function of a power screwdriver is to drive screws into different surfaces without the need for excessive manual effort. It can be used for a wide range of applications, including assembling furniture, installing fixtures, and building wooden structures.
Design:
Power screwdrivers come in various designs, but the most common type consists of a handheld tool with a pistol grip handle. They typically have a chuck or a bit holder at the front, where different types of screwdriver bits can be attached. The body of the screwdriver houses the motor, power source, and controls.
Power Source:
Power screwdrivers are generally powered by electricity, either from an electrical outlet or a rechargeable battery. Corded models offer consistent power supply, while cordless models provide mobility and convenience.
Torque:
Torque refers to the rotational force produced by the power screwdriver. Power screwdrivers usually have adjustable torque settings, allowing users to control the amount of force applied to the screws. This feature is particularly useful when working with delicate materials that require careful handling.
Speed:
Power screwdrivers offer variable speed options, allowing users to adjust the rotational speed according to the task at hand. Higher speeds are suitable for tasks that require quick and efficient screwdriving, while lower speeds are preferred for more precise and controlled applications.
Accuracy:
Power screwdrivers are generally designed to provide reliable and accurate screwdriving. The adjustable torque settings and variable speed options contribute to improved accuracy, as users can customize the tool’s performance to match the requirements of each task.
Versatility:
Power screwdrivers are highly versatile tools that can be used for various applications. They are compatible with different types and sizes of screwdriver bits, making them suitable for driving screws of different shapes and materials.
Ease of Use:
Power screwdrivers are user-friendly tools that are relatively easy to operate. The ergonomic design, lightweight construction, and comfortable grip contribute to reduced fatigue during prolonged use. Additionally, power screwdrivers often feature intuitive controls, making them accessible to users of all skill levels.
Size and Weight:
Power screwdrivers come in different sizes and weights, allowing users to choose a tool that fits their preferences and needs. Compact and lightweight models are particularly popular for their portability and maneuverability in tight spaces.
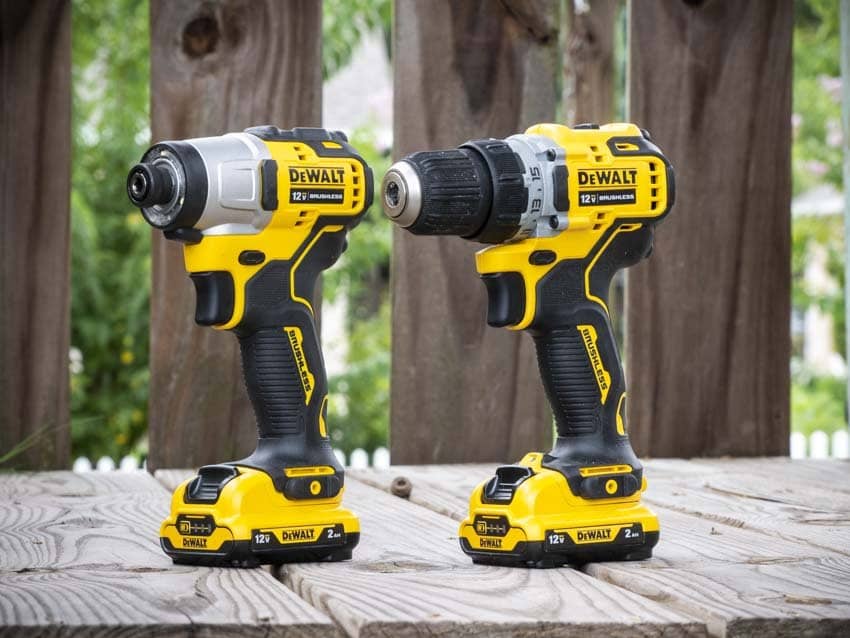

Impact Driver
Definition:
An impact driver is a powerful tool specifically designed for driving screws and loosening bolts. Unlike a power screwdriver, an impact driver combines a rotational force with concussive blows, providing enhanced driving power.
Function:
The main function of an impact driver is to drive screws quickly and efficiently using the combination of rotation and impacts. It is particularly effective for tasks involving long screws, stubborn fasteners, or challenging materials. The impact action helps prevent the bit from stripping or damaging the screw head.
Design:
Impact drivers have a similar overall design to power screwdrivers, with a pistol grip handle and a front chuck for attaching bits. However, they have a distinct hammering mechanism inside the tool that delivers the concussive blows. This mechanism allows for the quick transmission of torque to the screw, reducing the risk of the bit slipping or the screw getting stuck.
Power Source:
Like power screwdrivers, impact drivers can be powered by electricity or rechargeable batteries. Corded impact drivers offer continuous power supply, while cordless models provide greater mobility and flexibility.
Torque:
Impact drivers are known for their high torque output, which enables them to handle tough screwdriving tasks. They generate rotational force by combining the rotation of the motor with the impacts generated by the hammering mechanism.
Speed:
Impact drivers typically offer multiple speed settings, allowing users to adjust the rotational speed according to the task at hand. Higher speeds are suitable for quick and efficient screwdriving, while lower speeds provide better control and precision.
Accuracy:
Due to their high torque and concussive blows, impact drivers may not offer the same level of precision as power screwdrivers, especially in delicate applications. However, the impact action helps prevent the bit from slipping or damaging the screw head, ensuring reliable and secure screwdriving in most situations.
Versatility:
While impact drivers excel at driving screws, their functionality is limited compared to power screwdrivers. They are specifically designed for high-torque tasks and may not be as suitable for applications that require low torque or precise control.
Ease of Use:
Impact drivers are generally easy to use, thanks to their ergonomic design and comfortable grips. The concussive blows generated by the hammering mechanism significantly reduce the amount of manual force required from the user, making tasks less physically demanding.
Size and Weight:
Impact drivers come in various sizes and weights, providing users with options to suit their preferences and needs. Although they tend to be slightly heavier than power screwdrivers due to the additional hammering mechanism, many models are still compact and manageable for extended use.
In conclusion, while both power screwdrivers and impact drivers are used for driving screws, they differ significantly in their design, functionality, and purpose. Power screwdrivers offer versatility, accuracy, and adjustability, making them suitable for a wide range of screwdriving tasks. Impact drivers, on the other hand, provide higher torque and use concussive blows to handle challenging applications, making them ideal for heavy-duty tasks and stubborn fasteners. Understanding the differences between these two tools will help you choose the right one for your specific project or needs.